
Бесплатный фрагмент - Грамматика английского языка для старших классов
Системный курс с примерами и практикой
Предисловие
Дорогие читатели,
Я рада представить вам эту книгу — комплексное пособие по грамматике английского языка для старших классов. Моей целью было создать материал, который не только объясняет правила, но и помогает использовать их в реальной речи.
Изучение грамматики часто воспринимается как скучное повторение правил, однако знание структур языка — это ключ к уверенной и правильной коммуникации. В этой книге каждая глава построена так, чтобы сочетать теорию, примеры, историю на английском языке и практические упражнения. Такой подход позволяет закреплять знания постепенно, видеть их применение в повседневных ситуациях и развивать навыки письма и говорения одновременно.
Особое внимание уделено повторению и систематизации материала. Грамматические конструкции представлены в контексте, а полезные слова, выражения и идиомы помогают расширять словарный запас и делать речь более естественной. Я постаралась подобрать темы и примеры, которые будут интересны современным подросткам, и которые помогут легко запомнить основные правила.
Эта книга предназначена для самостоятельного изучения, а также может быть использована как вспомогательный материал для занятий в классе. Я надеюсь, что она станет вашим надежным помощником на пути к свободному владению английским языком. Помните, что грамматика — это не набор сложных правил, а инструмент для общения, творчества и уверенности в языке.
Желаю вам успехов, терпения и удовольствия от изучения английского!
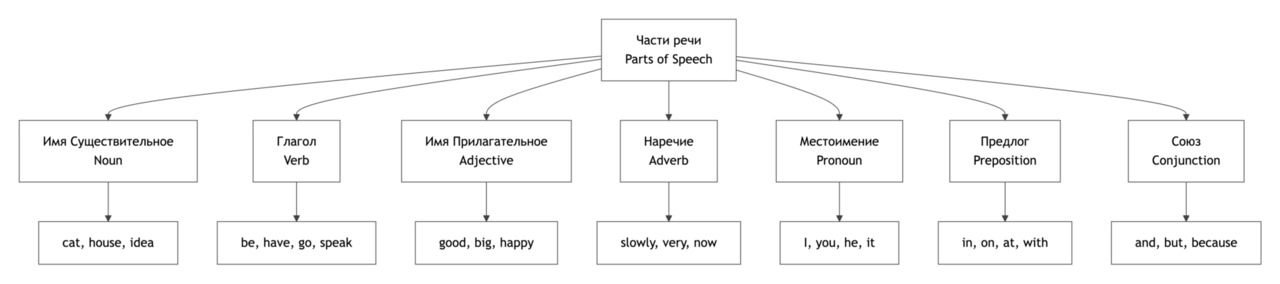
Parts of Speech in English
Grammar Focus
В английском языке слова делятся на части речи в зависимости от их функции в предложении. Знание частей речи помогает правильно строить предложения, понимать тексты и избегать типичных грамматических ошибок, особенно в заданиях ОГЭ и ЕГЭ.
Основные части речи в английском языке:
Noun (существительное) — называет людей, предметы, места, идеи.
student — ученик, city — город
Verb (глагол) — обозначает действие или состояние.
study — учиться, be — быть
Adjective (прилагательное) — описывает существительное.
interesting — интересный
Adverb (наречие) — описывает глагол, прилагательное или другое наречие.
quickly — быстро
Pronoun (местоимение) — заменяет существительное.
he — он, they — они
Preposition (предлог) — показывает связь между словами.
in — в, on — на
Conjunction (союз) — соединяет слова или части предложения.
and — и, because — потому что
Article (артикль) — используется перед существительными.
a, an, the
Примеры:
The student reads carefully. — Ученик читает внимательно.
She is very confident today. — Сегодня она очень уверена.
Советы для школьников:
Определяй часть речи по функции слова в предложении, а не по переводу.
Обращай внимание на типичные суффиксы (-ly, -tion, -ment).
Story
English is a flexible and logical language, but it becomes clear only when students understand how words work together. Every morning, a senior student opens a textbook and sees familiar words, but each of them has a specific role. A noun names an idea, a verb shows an action, and an adjective adds detail. Without these parts of speech, communication would be impossible.
During lessons, students often notice that the same word can belong to different parts of speech. For example, a word may describe a person in one sentence and an action in another. This makes English both challenging and interesting. A careful learner pays attention to position and meaning, not only to form.
At home, the student reads articles, watches videos, and writes short texts. Step by step, grammar becomes more natural. Prepositions help connect ideas, conjunctions organize thoughts, and adverbs explain how actions happen. Articles may seem small, but they play an important role in meaning.
With practice, the language stops being a list of rules. It turns into a system where every word has its place. Understanding parts of speech gives students confidence and helps them express ideas clearly in real-life situations and exams.
Useful Words and Expressions
part of speech — часть речи
function — функция
role — роль
meaning — значение
position — позиция
action — действие
description — описание
detail — деталь
communication — общение
learner — учащийся
careful — внимательный
connect ideas — связывать идеи
organize thoughts — упорядочивать мысли
step by step — шаг за шагом
confident — уверенный
real-life situations — реальные жизненные ситуации
Exercises
Exercise 1. Match the words with their parts of speech.
quickly
student
and
interesting
they
a) adjective
b) noun
c) conjunction
d) pronoun
e) adverb
Exercise 2. Choose the correct answer.
Which part of speech describes a noun?
a) Verb
b) Adjective
c) Preposition
Which word is a conjunction?
a) because
b) very
c) book
Which sentence contains an adverb?
a) She reads books.
b) He is a student.
c) They work carefully.
Exercise 3. Answer the questions.
Why is it important to understand parts of speech when learning English?
How do parts of speech help you in reading English texts?
Which part of speech is the most difficult for you and why?
How can knowing parts of speech help you in exams?
How often do you pay attention to word position in a sentence?
Answer Key
Exercise 1
1 — e
2 — b
3 — c
4 — a
5 — d
Exercise 2
1 — b
2 — a
3 — c
Exercise 3 (Sample Answers)
Understanding parts of speech is important because it helps me see how words function in a sentence and build correct structures. It also reduces grammar mistakes.
Parts of speech help me understand the meaning of sentences faster. I can identify key words and their roles in the text.
The most difficult part of speech for me is the article. It is challenging because articles do not exist in my native language.
Knowing parts of speech helps me complete grammar tasks correctly in exams. It allows me to choose the right word form.
I usually pay attention to word position when I read or write in English. It helps me understand the sentence structure better.
Mini Tips
Учите новые слова сразу с указанием части речи.
Подчёркивайте в текстах существительные, глаголы и прилагательные разными цветами.
При выполнении заданий сначала определите часть речи, а затем выбирайте форму слова.
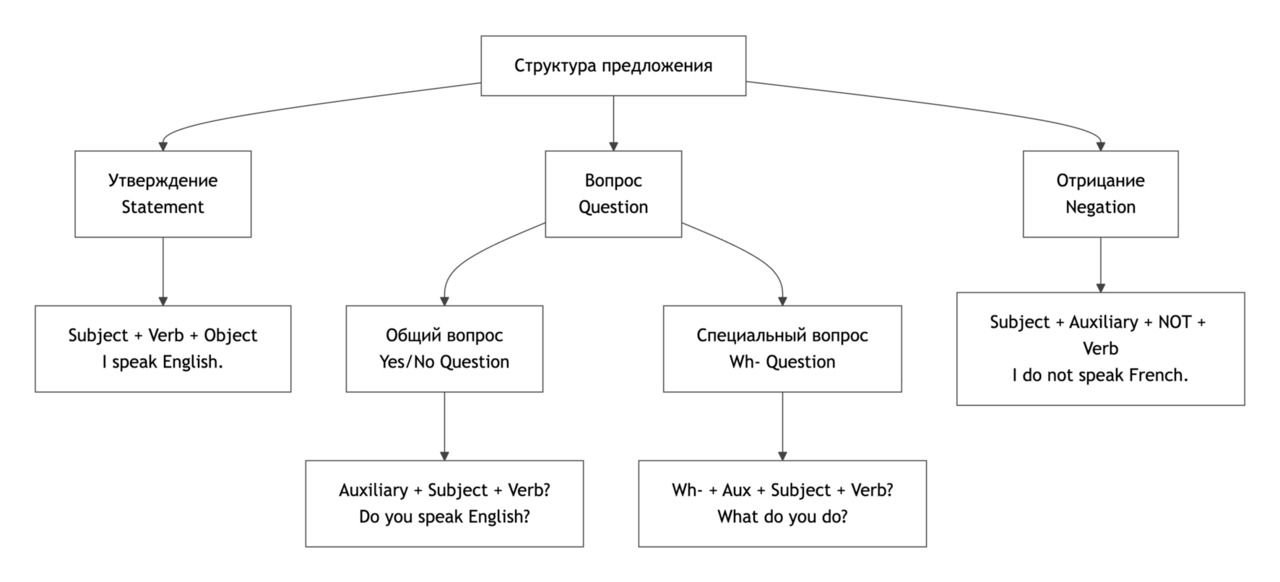
Sentence Structure: Statements, Questions, Negatives
Grammar Focus
В английском языке порядок слов в предложении играет ключевую роль. В отличие от русского, английский язык имеет фиксированную структуру предложения, и изменение порядка слов может изменить смысл или сделать предложение неправильным.
1. Statements (утвердительные предложения)
Базовый порядок слов:
Subject + Verb + Object
She reads books every day. — Она читает книги каждый день.
They live in a small town. — Они живут в маленьком городе.
2. Questions (вопросительные предложения)
В большинстве случаев используется вспомогательный глагол:
Auxiliary verb + Subject + Main verb
Do you like English? — Тебе нравится английский?
Is he at home now? — Он сейчас дома?
Вопросительные слова (what, where, why, how) ставятся в начале предложения:
Where do you live? — Где ты живёшь?
3. Negatives (отрицательные предложения)
Отрицание образуется с помощью not:
Subject + Auxiliary verb + not + Main verb
She does not understand the rule. — Она не понимает правило.
They are not ready. — Они не готовы.
Советы для школьников:
В английском предложении всегда есть подлежащее.
В вопросах и отрицаниях важно определить вспомогательный глагол.
Не переносите порядок слов в русском языке напрямую в английский.
Story
Every language has its own logic, and English sentence structure follows clear rules. A student who understands this logic feels more confident while reading and writing. In a simple statement, the subject comes first, followed by the verb. This structure makes ideas easy to follow.
When the student wants to ask a question, the sentence changes its form. An auxiliary verb moves to the beginning, and the word order becomes different. At first, this change seems unusual, but with time it feels natural. Questions help people get information, show interest, and keep communication active.
Negatives also follow a clear pattern. The word «not» appears after the auxiliary verb and changes the meaning of the sentence completely. A small word can turn a positive idea into a negative one.
During everyday activities, the student notices these structures everywhere. Short messages, articles, and videos all use the same basic patterns. Step by step, the learner stops translating from the native language and starts thinking in English. Understanding statements, questions, and negatives helps build clear sentences and express thoughts accurately in daily situations.
Useful Words and Expressions
sentence structure — структура предложения
word order — порядок слов
statement — утвердительное предложение
question — вопрос
negative — отрицание
subject — подлежащее
auxiliary verb — вспомогательный глагол
main verb — основной глагол
follow rules — следовать правилам
change meaning — менять значение
ask for information — спрашивать информацию
everyday activities — повседневные занятия
feel confident — чувствовать уверенность
express thoughts — выражать мысли
step by step — шаг за шагом
Exercises
Exercise 1. Choose the correct sentence.
a) Likes she music.
b) She likes music.
a) Do you understand this rule?
b) Understand you this rule?
a) They not are ready.
b) They are not ready.
Exercise 2. Multiple choice.
Which sentence is a question?
a) She works at home.
b) Does she work at home?
c) She does work at home.
Where is the word not placed in a negative sentence?
a) Before the subject
b) After the auxiliary verb
c) At the end of the sentence
Which sentence has correct word order?
a) Always he is late.
b) He is always late.
c) Is always he late.
Exercise 3. Answer the questions.
How does English word order help you understand sentences?
When do you usually ask questions in English?
Why are auxiliary verbs important in questions?
How do negative sentences change the meaning of ideas?
How often do you check word order when you write in English?
Answer Key
Exercise 1
1 — b
2 — a
3 — b
Exercise 2
1 — b
2 — b
3 — b
Exercise 3 (Sample Answers)
English word order helps me understand who does the action and what happens in the sentence. It makes ideas clear and logical.
I usually ask questions when I want to get information or clarify details. Questions help me continue communication.
Auxiliary verbs are important because they help form correct questions. Without them, the sentence structure would be incorrect.
Negative sentences change the meaning by showing that an action does not happen. They help express disagreement or absence of action.
I often check word order when I write in English. It helps me avoid mistakes and sound more natural.
Mini Tips
Запоминай базовую модель: Subject + Verb + Object.
В вопросах сначала ищи вспомогательный глагол.
Проверяй отрицательные предложения: одного not достаточно.
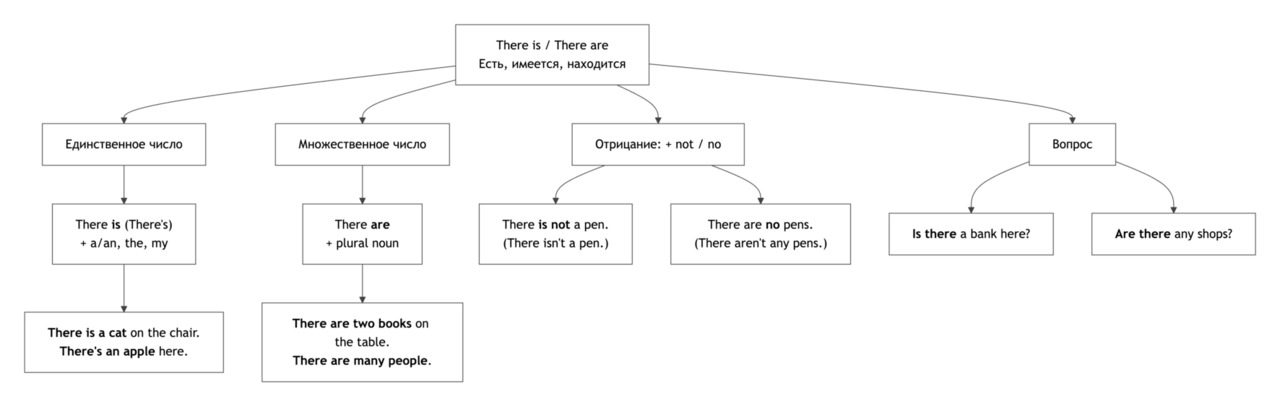
There Is / There Are
Grammar Focus
Конструкция there is / there are используется, чтобы сказать, что что-то существует или находится в каком-то месте. Она помогает вводить новую информацию и часто используется в описаниях комнат, городов, мест и ситуаций.
Форма и употребление
There is — с существительными в единственном числе и с неисчисляемыми существительными.
There are — с существительными во множественном числе.
Примеры:
There is a book on the table. — На столе есть книга.
There is some water in the bottle. — В бутылке есть немного воды.
There are two windows in the room. — В комнате есть два окна.
Вопросы и отрицания
Is there …? / Are there …?
Is there a problem? — Есть проблема?
Are there any students here? — Здесь есть ученики?
There is not / There are not
There is not enough time. — Недостаточно времени.
There are not any mistakes. — Ошибок нет.
Советы для школьников:
После there is / there are важно смотреть на существительное, а не на обстоятельство места.
В отрицаниях и вопросах часто используются слова any и much / many.
Не путайте there is с it is: первое говорит о наличии, второе — о конкретном предмете.
Story
There is a quiet street near the city center where many students like to spend their free time. There are small cafés, bookshops, and comfortable places to sit and relax. In the morning, there is usually fresh air and very little noise.
In one of the cafés, there is a large window with a view of the street. There are people reading, working, or simply watching others pass by. On the tables, there are notebooks, cups of coffee, and phones. There is always something interesting to notice.
In the afternoon, there are more visitors. There is music in the background, and there are friendly faces everywhere. For many students, this place feels safe and familiar. There is no pressure, and there are no strict rules.
By the evening, there are fewer people, but there is still a calm atmosphere. There are soft lights, and there is time to think and plan. For students who enjoy peaceful places, there is nothing better than this street and its simple rhythm of life.
Useful Words and Expressions
there is / there are — есть, имеется
quiet street — тихая улица
city center — центр города
free time — свободное время
fresh air — свежий воздух
noise — шум
café — кафе
view — вид
pass by — проходить мимо
in the background — на фоне
familiar — знакомый
atmosphere — атмосфера
pressure — давление
peaceful — спокойный
rhythm of life — ритм жизни
notice — замечать
Exercises
Exercise 1. Choose the correct option.
There ___ a book on the desk.
a) are
b) is
There ___ many students in the room.
a) is
b) are
There ___ any milk in the fridge.
a) isn’t
b) aren’t
___ there any questions?
a) Is
b) Are
Exercise 2. Multiple choice.
Which sentence is correct?
a) There is two windows in the room.
b) There are two windows in the room.
c) There have two windows in the room.
When do we use there is?
a) With plural nouns
b) With singular and uncountable nouns
c) With all nouns
Which sentence shows absence?
a) There is a problem.
b) There are many ideas.
c) There is no time.
Exercise 3. Answer the questions.
What places are there near your home?
Is there a place where you like to relax? Why?
Are there any quiet places you visit regularly?
What is there on your desk right now?
Are there any places you would like to visit in your city?
Answer Key
Exercise 1
1 — b
2 — b
3 — a
4 — b
Exercise 2
1 — b
2 — b
3 — c
Exercise 3 (Sample Answers)
There are several shops and a small park near my home. There is also a bus stop close to my building.
Yes, there is a quiet park where I like to relax. There is fresh air, and there are not many people there.
Yes, there are a few quiet places that I visit regularly. There is a small café where I feel comfortable.
There is a laptop and a notebook on my desk. There are also a few pens next to them.
Yes, there are some places I would like to visit in my city. There is a museum that seems very interesting.
Mini Tips
Сначала смотри на существительное после there.
Используй there is / there are для описаний и введения новой информации.
В одном абзаце старайся повторять конструкцию — так она лучше запоминается.
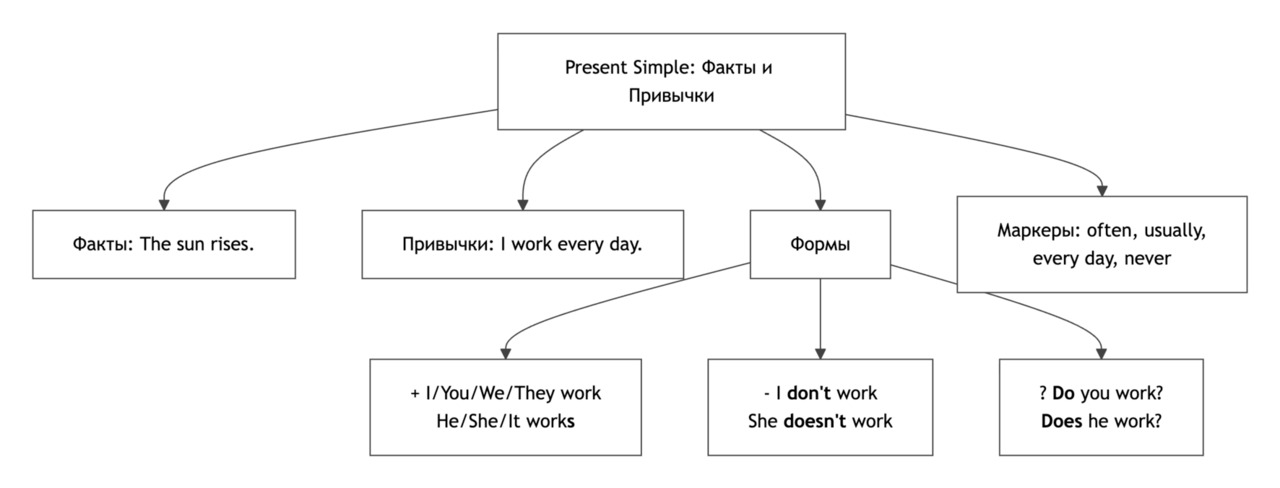
Present Simple: Facts and Habits
Grammar Focus
Present Simple используется для выражения фактов, привычек и регулярных действий. Это самая базовая форма глагола для описания того, что происходит обычно или всегда.
Структура утвердительных предложений
Subject + base verb (+ -s / -es для he, she, it)
I read every day. — Я читаю каждый день.
She plays the piano well. — Она хорошо играет на пианино.
Правила:
Для 3-го лица единственного числа (he, she, it) добавляем -s или -es:
he watches TV, she studies English.
С глаголами, оканчивающимися на -o, -ch, -sh, -ss, -x, добавляем -es.
Вопросы и отрицания
Do / Does + Subject + Base Verb
Do you like coffee? — Ты любишь кофе?
Does he play football? — Он играет в футбол?
Отрицания:
I do not (don’t) eat meat. — Я не ем мясо.
She does not (doesn’t) watch TV in the morning. — Она не смотрит телевизор утром.
Советы для школьников:
Запоминай, что 3-е лицо требует -s / -es — это самая частая ошибка.
Используй Present Simple для привычек, повторяющихся действий и общих фактов.
В вопросах и отрицаниях всегда нужен вспомогательный глагол do / does.
Story
Every morning, a student wakes up at six o’clock. He brushes his teeth, washes his face, and makes breakfast. He always drinks a cup of tea before leaving the house. At school, he studies English, mathematics, and science. Every lesson begins with a short review of yesterday’s material.
The student plays football after school. He usually practices with his friends twice a week. On weekends, he visits his grandparents and helps them in the garden. His mother always prepares a meal on Sunday, and the family eats together.
In the evenings, the student reads books or watches short educational videos. He does not watch TV for a long time. His routine is simple but productive. He believes that small daily habits bring good results. Each day, he learns something new, and every evening, he checks his homework carefully.
Through these simple actions, the student develops discipline. The Present Simple tense is useful because it describes these facts clearly. Everyone can understand what usually happens in his life.
Useful Words and Expressions
routine — распорядок
habit — привычка
every day — каждый день
usually — обычно
sometimes — иногда
always — всегда
after school — после школы
in the evening — вечером
make breakfast — готовить завтрак
brush teeth — чистить зубы
wash face — умываться
practice sports — заниматься спортом
productive — продуктивный
small actions — маленькие действия
review material — повторять материал
check homework — проверять домашнее задание
believe — верить
learn something new — изучать что-то новое
Exercises
Exercise 1. Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb.
She ___ (play) the piano every day.
I ___ (not / watch) TV in the morning.
He ___ (study) English at school.
They ___ (go) to the park on weekends.
My mother ___ (cook) dinner on Sundays.
Exercise 2. Multiple choice.
Which sentence is correct?
a) He play football every week.
b) He plays football every week.
c) He playing football every week.
How do we form a question for «she reads books»?
a) She does reads books?
b) Does she read books?
c) Does she reads books?
Which word shows habit?
a) yesterday
b) always
c) now
Exercise 3. Answer the questions.
What is your daily routine?
Which habits do you do every day?
How often do you read or study English?
Who helps you at home, and what do they do?
What small actions do you think are important for a productive day?
Answer Key
Exercise 1
1 — plays
2 — do not (don’t) watch
3 — studies
4 — go
5 — cooks
Exercise 2
1 — b
2 — b
3 — b
Exercise 3 (Sample Answers)
My daily routine includes waking up at seven, having breakfast, and going to school. I usually study in the evening.
I always brush my teeth and wash my face every morning. I usually read for 20 minutes before school.
I study English every day, and I read English books several times a week.
My parents help me at home. My mother cooks meals, and my father fixes things if needed.
Small actions like making the bed, doing homework, and planning the day are important for a productive day.
Mini Tips
Для 3-го лица всегда добавляй -s / -es.
Используй do / does в вопросах и отрицаниях.
Опиши свой день простыми фактами — так проще запомнить Present Simple.
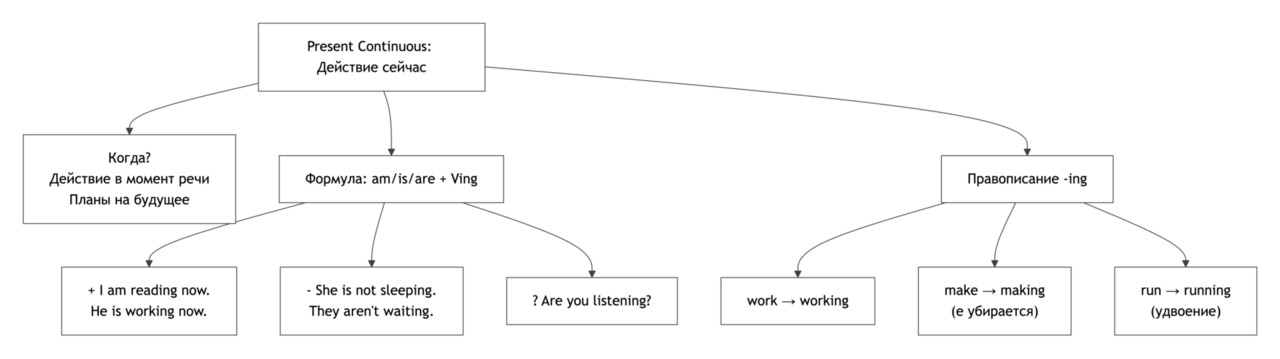
Present Continuous: Actions in Progress
Grammar Focus
Present Continuous описывает действия, которые происходят в момент речи, а также временные или развивающиеся процессы. Этот строй часто используется для описания событий «сейчас» и ближайшего будущего.
Структура утвердительных предложений
Subject + am / is / are + Verb-ing
I am reading a book. — Я читаю книгу (сейчас).
She is watching a video. — Она смотрит видео.
They are playing football. — Они играют в футбол.
Правила:
Глагол всегда в форме -ing.
Вспомогательный глагол am / is / are зависит от подлежащего:
I → am
he, she, it → is
we, you, they → are
Вопросы и отрицания
Вопрос: Am / Is / Are + Subject + Verb-ing?
Are you studying now? — Ты сейчас учишься?
Is he working in the garden? — Он работает в саду?
Отрицание: Subject + am / is / are + not + Verb-ing
I am not sleeping. — Я не сплю.
She is not playing the piano. — Она не играет на пианино.
Советы для школьников:
Используй Present Continuous только для действий, происходящих сейчас или временно.
Не забывай вспомогательный глагол.
Добавляй -ing к основному глаголу.
Story
It is a sunny afternoon, and a student is sitting at his desk. He is writing in his notebook while listening to music. His sister is drawing a picture nearby, and their dog is sleeping quietly on the floor. Outside, the birds are singing, and people are walking along the street.
In the kitchen, the mother is cooking dinner. She is chopping vegetables and stirring soup at the same time. The father is reading a newspaper in the living room. Sometimes, the student is helping him by bringing the letters from the mailbox.
At school, students are practicing for a school play. Some are acting, while others are preparing props. The teacher is giving instructions and correcting mistakes. Everyone is busy, but the atmosphere is calm and friendly.
Even though the day is ordinary, many things are happening at the same time. By observing actions around him, the student understands how Present Continuous shows activities in progress. He notices small details and enjoys seeing how people act in real life. Present Continuous helps him describe what is happening right now and communicate clearly.
Useful Words and Expressions
at the moment — в данный момент
right now — прямо сейчас
action in progress — действие в процессе
temporary — временный
desk — письменный стол
notebook — тетрадь
draw a picture — рисовать картину
quietly — тихо
outside — снаружи
bird — птица
walk along — гулять вдоль
chop vegetables — нарезать овощи
stir soup — мешать суп
read a newspaper — читать газету
help — помогать
observe — наблюдать
notice details — замечать детали
describe actions — описывать действия
Exercises
Exercise 1. Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb.
I ___ (write) a letter at the moment.
She ___ (not / watch) TV now.
They ___ (play) football outside.
The teacher ___ (give) instructions to the students.
He ___ (sleep) on the sofa.
Exercise 2. Multiple choice.
Which sentence is correct?
a) He is play football now.
b) He are playing football now.
c) He is playing football now.
How do we form a question in Present Continuous?
a) Verb-ing + Subject + am / is / are
b) Am / Is / Are + Subject + Verb-ing
c) Subject + am / is / are + Verb-ing?
Which word shows that an action is happening right now?
a) usually
b) at the moment
c) every day
Exercise 3. Answer the questions.
What are you doing right now?
Who is doing something interesting around you?
Are you observing actions around you today? What do you notice?
Is anyone helping you at the moment? How?
What temporary activities do you usually do during the week?
Answer Key
Exercise 1
1 — am writing
2 — is not (isn’t) watching
3 — are playing
4 — is giving
5 — is sleeping
Exercise 2
1 — c
2 — b
3 — b
Exercise 3 (Sample Answers)
I am writing in my notebook and listening to music right now.
My friend is reading a book, and my brother is playing with his toys.
Yes, I am observing the people in my house. I notice small actions, like someone watering the plants.
My mother is helping me by making lunch, and my sister is explaining homework tasks.
During the week, I am attending extra lessons and playing football with friends. These are temporary activities.
Mini Tips
Вспомогательный глагол am / is / are обязателен.
Глагол всегда в форме -ing.
Используй Present Continuous, когда хочешь подчеркнуть, что действие происходит прямо сейчас или временно.
Present Simple vs Present Continuous
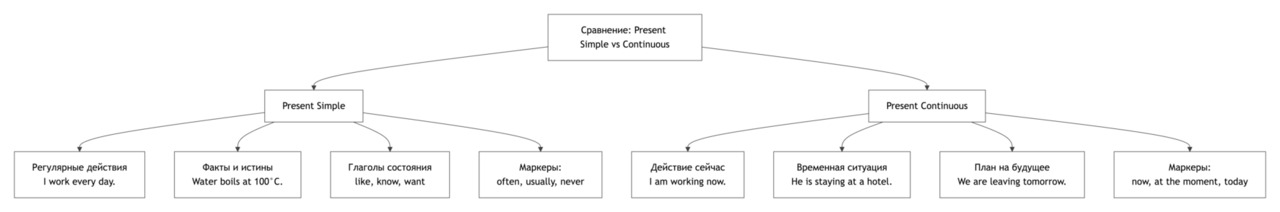
Grammar Focus
Present Simple и Present Continuous часто используются вместе, но выполняют разные функции.
Present Simple описывает регулярные действия, привычки и факты. Оно показывает, что что-то происходит обычно, всегда или часто. Например:
I read books every day. — Я читаю книги каждый день.
She plays football on weekends. — Она играет в футбол по выходным.
Present Continuous описывает действия, происходящие прямо сейчас, или временные процессы. Оно указывает на события, которые не являются постоянными. Например:
I am reading a book now. — Я читаю книгу прямо сейчас.
She is playing football at the park today. — Она играет в футбол сегодня в парке.
Как отличить:
Если действие повторяется или происходит регулярно — Present Simple.
Если действие происходит в момент речи или временно — Present Continuous.
В вопросах и отрицаниях всегда нужно помнить про вспомогательные глаголы: do / does для Present Simple и am / is / are для Present Continuous.
Слова-маркеры помогают определить время:
Present Simple: every day, usually, often, sometimes
Present Continuous: now, at the moment, today
Story
It is a typical weekday morning. A student usually wakes up at seven o’clock. He eats breakfast, brushes his teeth, and leaves for school. Every day, he studies English, mathematics, and science. These activities are part of his regular routine.
However, today is different. He is reading a new book in the living room. His sister is drawing a picture on the table, and their dog is sleeping nearby. Outside, the neighbors are planting flowers in the garden. Normally, these actions happen at different times, but right now, many things are happening simultaneously.
During lessons, the student notices the difference between regular activities and actions in progress. His teacher explains that Present Simple describes habits, while Present Continuous describes current activities. He practices forming questions and negatives for both tenses.
By the evening, he is reflecting on his day. He realizes that combining Present Simple and Present Continuous helps him describe his life clearly. He can talk about routines, temporary events, and what is happening at this very moment. Understanding the difference between these two tenses makes his English more precise and expressive.
Useful Words and Expressions
regular routine — обычный распорядок
habit — привычка
everyday activities — повседневные действия
temporary — временный
at the moment — в данный момент
right now — прямо сейчас
unusual — необычный
different — разный
reflect — размышлять
notice — замечать
describe clearly — описывать ясно
current activities — текущие действия
neighbor — сосед
combine — сочетать
precise — точный
expressive — выразительный
simultaneously — одновременно
normally — обычно
Exercises
Exercise 1. Fill in the blanks with the correct tense (Present Simple or Present Continuous).
I usually ___ (go) to school at 8 a.m., but today I ___ (walk) because my bus is late.
She ___ (study) English every day.
Listen! The birds ___ (sing) outside.
My parents ___ (work) in the garden every weekend, but today they ___ (rest).
He ___ (play) football now, but usually he ___ (read) books at this time.
Exercise 2. Multiple choice.
Which sentence shows a temporary action?
a) I drink tea every morning.
b) I am drinking tea now.
Which sentence is a habit?
a) She is reading a new book.
b) She reads books every evening.
Choose the correct form:
He usually ___ (watch) TV, but today he ___ (study).
a) watches / is studying
b) watch / studies
c) is watching / studies
Exercise 3. Answer the questions.
What do you usually do in the morning?
What are you doing right now?
Do you have any temporary activities today? What are they?
Who in your family has regular habits, and what are they?
How do you know when to use Present Simple or Present Continuous?
Answer Key
Exercise 1
1 — go / am walking
2 — studies
3 — are singing
4 — work / are resting
5 — is playing / reads
Exercise 2
1 — b
2 — b
3 — a
Exercise 3 (Sample Answers)
I usually wake up at seven, have breakfast, and go to school in the morning.
I am writing and listening to music right now.
Yes, I am attending an online lesson today, which is temporary.
My father has regular habits: he drinks coffee every morning and goes for a walk in the evening.
I look at the context: if it is an everyday habit or fact, I use Present Simple; if it is happening right now or temporarily, I use Present Continuous.
Mini Tips
Обращай внимание на слова-маркеры времени: every day, usually → Present Simple; now, at the moment, today → Present Continuous.
Сравнивай действия: привычка или текущее событие?
Практикуй обе формы вместе, описывая свой день и события прямо сейчас.
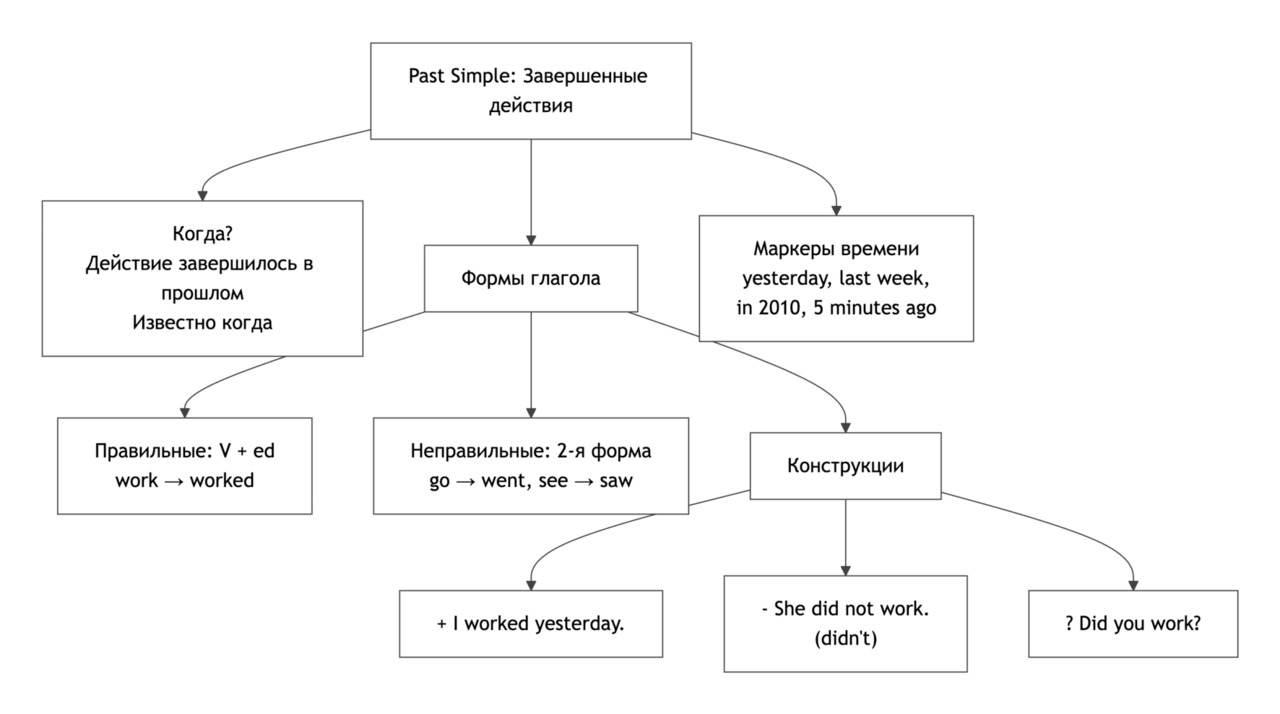
Past Simple: Completed Actions in the Past
Grammar Focus
Past Simple используется для действий, которые завершились в прошлом. Оно описывает события с конкретным временем или прошлые привычки.
Форма утвердительных предложений
Subject + Past Verb
Для правильных глаголов добавляется -ed:
I visited my grandparents yesterday. — Я посетил своих бабушку и дедушку вчера.
She watched a film last night. — Она посмотрела фильм прошлым вечером.
Неправильные глаголы имеют особую форму в Past Simple:
go → went, have → had, see → saw
I went to the park. — Я ходил в парк.
Вопросы и отрицания
Вопрос: Did + Subject + Base Verb
Did you see that movie? — Ты видел тот фильм?
Отрицание: Subject + did not (didn’t) + Base Verb
I did not (didn’t) watch TV yesterday. — Я не смотрел телевизор вчера.
Советы для школьников:
Обязательно используй вспомогательный глагол did в вопросах и отрицаниях.
Для правильных глаголов добавляй -ed, а неправильные глаголы учи наизусть.
Часто встречаются слова-маркеры: yesterday, last week, in 2010, two days ago — они помогают определить Past Simple.
Story
Yesterday, a student had a very busy day. He woke up at seven o’clock and made breakfast for himself. After eating, he went to the park and met his friends. They played football for an hour and then walked around the city center.
In the afternoon, the student visited the library. He borrowed three books and read them quietly in the reading room. Later, he wrote a short story about his weekend. He didn’t feel tired because he enjoyed every activity.
In the evening, the student helped his parents with dinner. He chopped vegetables and set the table. After the meal, he watched a movie with his sister. They laughed and talked about the story in the film.
Before going to bed, he checked his homework and prepared his school bag for the next day. It was a productive day, and he felt satisfied. By reflecting on his day, he remembered all the actions he completed and learned how to use Past Simple to describe them clearly.
Useful Words and Expressions
yesterday — вчера
last night — прошлой ночью
last week — на прошлой неделе
two days ago — два дня назад
wake up — просыпаться
make breakfast — приготовить завтрак
go to the park — идти в парк
meet friends — встречаться с друзьями
play football — играть в футбол
walk around — гулять вокруг
visit the library — посетить библиотеку
borrow books — брать книги
read quietly — читать тихо
write a story — писать рассказ
help parents — помогать родителям
chop vegetables — нарезать овощи
set the table — накрывать на стол
feel tired — чувствовать усталость
productive day — продуктивный день
reflect — размышлять
Exercises
Exercise 1. Fill in the blanks with the correct past form of the verb.
Yesterday, I ___ (wake) up at 7 a.m.
She ___ (visit) her grandparents last week.
They ___ (play) football in the park.
I ___ (not / watch) TV yesterday.
We ___ (go) to the library and ___ (borrow) some books.
Exercise 2. Multiple choice.
Which sentence is correct?
a) I goed to school yesterday.
b) I went to school yesterday.
How do we form a question in Past Simple?
a) Did + Subject + Base Verb
b) Do + Subject + Base Verb
c) Subject + Verb-ed
Which word shows the action is in the past?
a) today
b) last week
c) now
Exercise 3. Answer the questions.
What did you do yesterday?
Did you meet anyone interesting last week?
Did you watch any movies recently? Which ones?
What homework did you do yesterday?
Did you help anyone at home recently? How?
Answer Key
Exercise 1
1 — woke
2 — visited
3 — played
4 — did not (didn’t) watch
5 — went / borrowed
Exercise 2
1 — b
2 — a
3 — b
Exercise 3 (Sample Answers)
Yesterday, I woke up at seven, had breakfast, and went to school. I played football with my friends after classes.
Yes, I met my cousin last week. We walked in the park together.
I watched a new film on Saturday. It was very interesting and funny.
I did my English homework and also solved some math exercises.
Yes, I helped my mother with cooking yesterday. I chopped vegetables and set the table.
Mini Tips
Слова-маркеры помогают определить Past Simple: yesterday, last night, last week, two days ago.
В вопросах и отрицаниях всегда используй вспомогательный глагол did.
Неправильные глаголы нужно учить отдельно, правильные образуются с -ed.
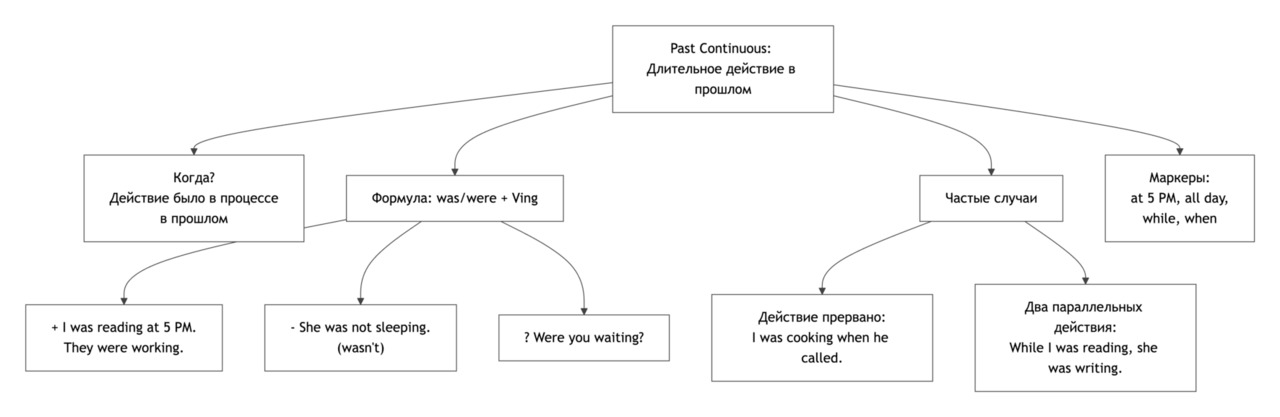
Past Continuous: Actions in Progress in the Past
Grammar Focus
Past Continuous используется для описания действий, которые происходили в определённый момент в прошлом. Оно показывает, что действие было в процессе, а не завершено.
Структура утвердительных предложений
Subject + was / were + Verb-ing
I was reading a book at 6 p.m. — Я читал книгу в 6 вечера.
She was watching TV when I called. — Она смотрела телевизор, когда я позвонил.
They were playing football in the park. — Они играли в футбол в парке.
Правила:
Используем was с I, he, she, it и were с we, you, they.
Глагол всегда в форме -ing.
Вопросы и отрицания
Вопрос: Was / Were + Subject + Verb-ing?
Was she studying at 7 p.m.? — Она училась в 7 вечера?
Отрицание: Subject + was / were + not + Verb-ing
I was not (wasn’t) sleeping. — Я не спал.
They were not (weren’t) playing football. — Они не играли в футбол.
Советы для школьников:
Past Continuous часто используется вместе с Past Simple, когда одно действие длилось, а другое произошло внезапно.
Слова-маркеры: at 6 p.m., while, when, yesterday evening.
Всегда добавляй -ing к глаголу и выбирай правильную форму was / were.
Story
Yesterday evening, a student was sitting at his desk and doing homework. His sister was listening to music in her room, and their dog was sleeping on the sofa. Outside, the rain was falling gently, and people were walking home with umbrellas.
While the student was writing a story, his father was cooking dinner in the kitchen. The mother was talking on the phone and making notes at the same time. Suddenly, the telephone rang. The student stopped writing, and his sister turned off the music. His father answered the call, and the dog woke up for a moment, then went back to sleep.
During the evening, many things were happening simultaneously. The student realized that Past Continuous helps describe actions that were in progress at a specific moment in the past. It also allows combining with Past Simple to show that one action interrupted another. By the end of the evening, the student felt satisfied with all the tasks he completed and the moments he observed.
Useful Words and Expressions
at 6 p.m. — в 6 вечера
yesterday evening — вчера вечером
while — в то время как
when — когда
do homework — делать домашнюю работу
sit at a desk — сидеть за столом
listen to music — слушать музыку
sleep — спать
fall gently — падать тихо
walk home — идти домой
cook dinner — готовить ужин
talk on the phone — разговаривать по телефону
make notes — делать заметки
stop writing — перестать писать
turn off music — выключить музыку
wake up — просыпаться
back to sleep — снова заснуть
actions in progress — действия в процессе
interrupted — прерванный
Exercises
Exercise 1. Fill in the blanks with the correct past continuous form.
I ___ (read) a book at 7 p.m. yesterday.
She ___ (not / watch) TV when I arrived.
They ___ (play) football while it was raining.
My parents ___ (cook) dinner at 6 p.m.
The dog ___ (sleep) on the sofa when the phone rang.
Exercise 2. Multiple choice.
Which sentence is correct?
a) I was play football yesterday evening.
b) I was playing football yesterday evening.
c) I were playing football yesterday evening.
Which word shows an action in progress in the past?
a) yesterday morning
b) while
c) last week
How do we form a negative in Past Continuous?
a) Subject + did not + Verb-ing
b) Subject + was / were + not + Verb-ing
c) Subject + was / were + Verb-ed
Exercise 3. Answer the questions.
What were you doing yesterday evening?
Was anyone in your family doing something interesting while you were busy?
Did something happen while you were doing your homework?
Which actions were happening at the same time in your house yesterday?
How can you combine Past Continuous with Past Simple to describe events?
Answer Key
Exercise 1
1 — was reading
2 — was not (wasn’t) watching
3 — were playing
4 — were cooking
5 — was sleeping
Exercise 2
1 — b
2 — b
3 — b
Exercise 3 (Sample Answers)
Yesterday evening, I was doing my homework and listening to music.
My sister was drawing a picture while I was studying.
Yes, the phone rang while I was writing my essay.
My parents were cooking, my sister was listening to music, and the dog was sleeping.
I can describe one action in progress with Past Continuous and show the action that interrupted it with Past Simple.
Mini Tips
Используй was / were + Verb-ing для действий, происходивших в прошлом в определённый момент.
Часто Past Continuous сочетается с Past Simple: одно действие длится, другое прерывает.
Слова-маркеры: while, when, at 6 p.m., yesterday evening помогают определить правильное время.
Past Simple vs Past Continuous
Grammar Focus
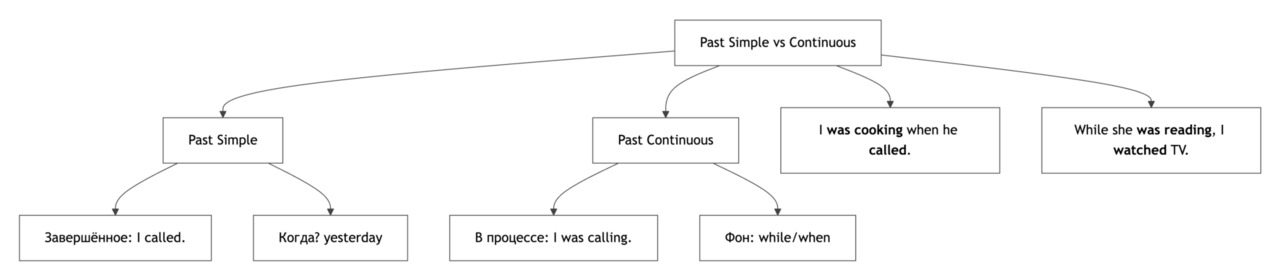
Past Simple и Past Continuous оба описывают события в прошлом, но имеют разные функции.
Past Simple используется для действий, которые завершились в прошлом. Оно показывает, что событие произошло в конкретный момент времени.
I visited my grandparents yesterday. — Я посетил бабушку и дедушку вчера.
She watched a film last night. — Она посмотрела фильм прошлой ночью.
Past Continuous описывает действия, которые происходили в процессе в прошлом. Оно показывает, что действие длилось в определённый момент и могло быть прервано другим событием.
I was reading a book at 6 p.m. — Я читал книгу в 6 вечера.
She was watching TV when I called. — Она смотрела телевизор, когда я позвонил.
Ключевое различие:
Если событие произошло и завершилось — Past Simple.
Если действие длилось и происходило в момент в прошлом — Past Continuous.
Часто одно действие в Past Continuous прерывается действием в Past Simple:
I was walking home when it started to rain. — Я шёл домой, когда начался дождь.
Слова-маркеры помогают понять, какое время использовать:
Past Simple: yesterday, last week, two days ago
Past Continuous: while, when, at 6 p.m., yesterday evening
Story
Yesterday, a student had an unusual day. In the morning, he visited his grandparents and played board games with them. Later, he went to the park. While he was walking, his sister was riding her bicycle nearby. Suddenly, it started to rain, and he ran home quickly.
At home, his father was cooking dinner when the student arrived. He was chopping vegetables while his mother was setting the table. The dog was sleeping on the sofa, and the cat was playing with a ball of yarn. During the evening, the student did his homework and watched a short video. While he was writing, the telephone rang. He answered the call and talked with his friend.
By the end of the day, the student reflected on all the things that happened. He realized that Past Simple helps describe completed actions, while Past Continuous shows what was in progress. Using both together, he could tell a story clearly, describing routines, interruptions, and simultaneous events in the past.
Useful Words and Expressions
yesterday — вчера
last week — на прошлой неделе
two days ago — два дня назад
while — в то время как
when — когда
at 6 p.m. — в 6 вечера
visit grandparents — посещать бабушку и дедушку
play board games — играть в настольные игры
walk home — идти домой
ride a bicycle — кататься на велосипеде
start to rain — начался дождь
cook dinner — готовить ужин
chop vegetables — нарезать овощи
set the table — накрывать на стол
sleep — спать
play with a ball of yarn — играть с клубком
do homework — делать домашнее задание
answer the call — ответить на звонок
reflect — размышлять
interruption — прерывание
Exercises
Exercise 1. Fill in the blanks with Past Simple or Past Continuous.
I ___ (watch) TV when my friend ___ (call) me.
Yesterday, we ___ (go) to the park while it ___ (rain) lightly.
She ___ (not / do) her homework yesterday because she ___ (play) outside.
At 7 p.m., I ___ (cook) dinner and my sister ___ (listen) to music.
He ___ (see) an accident while he ___ (walk) to school.
Exercise 2. Multiple choice.
Which sentence shows an action in progress interrupted by another?
a) I was reading a book when the phone rang.
b) I read a book yesterday.
Which word signals Past Continuous?
a) yesterday
b) while
c) last week
How do we describe completed actions?
a) Past Continuous
b) Past Simple
c) Both
Exercise 3. Answer the questions.
What did you do yesterday?
Were you doing anything interesting while someone else was busy?
Did anything happen that interrupted your activity recently?
What simultaneous actions did you notice at home yesterday?
How can you use Past Simple and Past Continuous together to tell a story?
Answer Key
Exercise 1
1 — was watching / called
2 — went / was raining
3 — did not (didn’t) do / was playing
4 — was cooking / was listening
5 — saw / was walking
Exercise 2
1 — a
2 — b
3 — b
Exercise 3 (Sample Answers)
Yesterday, I woke up, had breakfast, and went to school. I also played football with my friends.
Yes, I was doing my homework while my sister was listening to music.
The phone rang while I was writing an essay.
My parents were cooking dinner, my brother was reading, and the dog was sleeping at the same time.
I use Past Continuous to describe what was happening and Past Simple to show the actions that interrupted or completed it.
Mini Tips
Используй Past Continuous для действий, происходивших в процессе в прошлом, особенно если одно действие прерывается другим.
Past Simple показывает завершённые действия в прошлом.
Слова-маркеры: while, when, yesterday, at 6 p.m. помогают выбрать правильное время.
Практикуй обе формы вместе, описывая события и истории из прошлого.
Future Forms: Will, Be Going To, Present Continuous
Grammar Focus
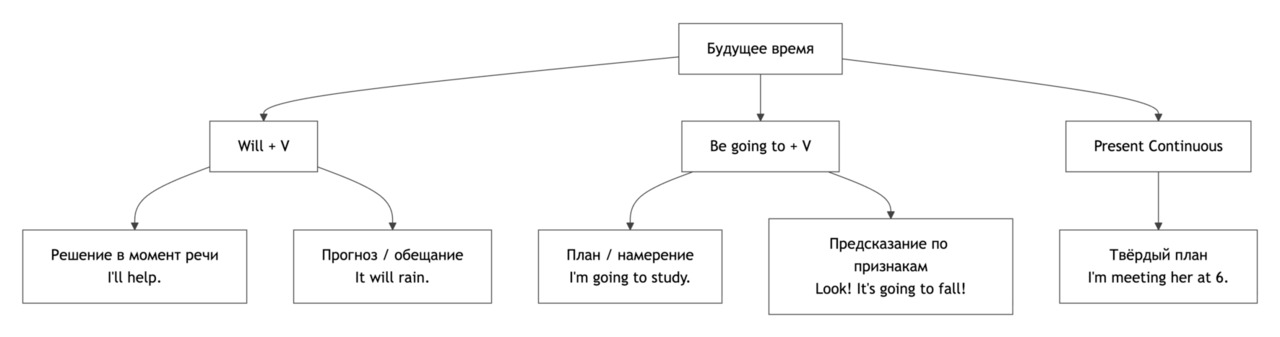
В английском языке будущее время можно выражать разными способами: Will, Be Going To и Present Continuous. Каждый вариант имеет своё использование.
1. Will
Используется для:
Спонтанных решений: I will help you with your homework. — Я помогу тебе с домашним заданием.
Предсказаний без явных доказательств: It will rain tomorrow. — Завтра будет дождь.
Обещаний или предложений: I will call you later. — Я позвоню тебе позже.
Структура: Subject + will + Base Verb
Отрицание: Subject + will not (won’t) + Base Verb
Вопрос: Will + Subject + Base Verb?
2. Be Going To
Используется для:
Намерений или планов: I am going to visit my friend this weekend. — Я собираюсь навестить друга на этих выходных.
Предсказаний с доказательствами: Look at the clouds! It’s going to rain. — Посмотри на облака! Скоро будет дождь.
Структура: Subject + am/is/are + going to + Base Verb
Отрицание: Subject + am/is/are not + going to + Base Verb
Вопрос: Am/Is/Are + Subject + going to + Base Verb?
3. Present Continuous for Future
Используется для:
Запланированных действий в ближайшем будущем: I am meeting my teacher tomorrow. — Я встречаюсь с учителем завтра.
Чаще всего сопровождается конкретным временем: at 6 p.m., tomorrow, next week.
Структура: Subject + am/is/are + Verb-ing
Отрицание: Subject + am/is/are not + Verb-ing
Вопрос: Am/Is/Are + Subject + Verb-ing?
Советы для школьников:
Will — для быстрых решений и предсказаний без доказательств.
Be Going To — для планов и предсказаний с доказательствами.
Present Continuous — для уже запланированных действий в ближайшем будущем.
Слова-маркеры помогают определить форму: tomorrow, next week, soon, look at…
Story
Tomorrow is going to be a busy day for a student. He is meeting his teacher in the morning to discuss his homework. After that, he is visiting his grandparents. He has planned this meeting for a long time and is very excited.
While he is walking to his grandparents’ house, he sees dark clouds in the sky. It looks like it will rain, he thinks. He decides to take an umbrella just in case. At home, his sister is packing her bag because she is going to travel to her friend’s house in the afternoon.
In the evening, the student is planning to study English. I will finish my exercises before dinner, he says to himself. He is confident that the day will be productive and enjoyable. By using different future forms, he can talk about his plans, intentions, and predictions clearly. Understanding these forms helps him describe the future accurately and express his ideas naturally.
Useful Words and Expressions
tomorrow — завтра
next week — на следующей неделе
soon — скоро
in the morning — утром
in the afternoon — днём
in the evening — вечером
meet a teacher — встречаться с учителем
discuss homework — обсуждать домашнее задание
visit grandparents — навещать бабушку и дедушку
plan — планировать
be excited — быть взволнованным
look at the sky — смотреть на небо
dark clouds — тёмные облака
take an umbrella — взять зонтик
travel to a friend’s house — поехать к другу
study English — заниматься английским
finish exercises — закончить упражнения
productive day — продуктивный день
intention — намерение
prediction — предсказание
Exercises
Exercise 1. Fill in the blanks with Will, Be Going To, or Present Continuous.
I ___ (help) you with your homework right now.
She ___ (visit) her friend tomorrow.
Look at the clouds! It ___ (rain) soon.
We ___ (meet) our teacher at 10 a.m. tomorrow.
I think he ___ (be) very happy with this news.
Exercise 2. Multiple choice.
Which sentence expresses a plan?
a) I will call you later.
b) I am going to visit my friend.
c) It will rain tomorrow.
Which sentence expresses a scheduled action?
a) I am meeting my teacher tomorrow.
b) I will decide now.
c) Look! It is going to snow.
Which word signals Be Going To for predictions?
a) evidence / look at…
b) tomorrow
c) next week
Exercise 3. Answer the questions.
What are you going to do tomorrow?
Are you meeting anyone soon? Who?
Will you help anyone with something in the near future?
What plans do you have for next week?
Can you predict something that will happen soon?
Answer Key
Exercise 1
1 — will help
2 — is going to visit
3 — will rain
4 — are meeting
5 — will be
Exercise 2
1 — b
2 — a
3 — a
Exercise 3 (Sample Answers)
Tomorrow, I am going to do my homework and play football with my friends.
Yes, I am meeting my teacher tomorrow to discuss my exercises.
I will help my sister with cleaning her room.
Next week, I am planning to visit my grandparents and study for my exams.
I think it will rain soon because the clouds are dark.
Mini Tips
Will — быстрые решения и предсказания без доказательств.
Be Going To — намерения и предсказания с доказательствами.
Present Continuous — запланированные действия в ближайшем будущем.
Слова-маркеры помогают определить правильную форму: tomorrow, next week, soon, at 6 p.m., look at ….
Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Grammar Focus
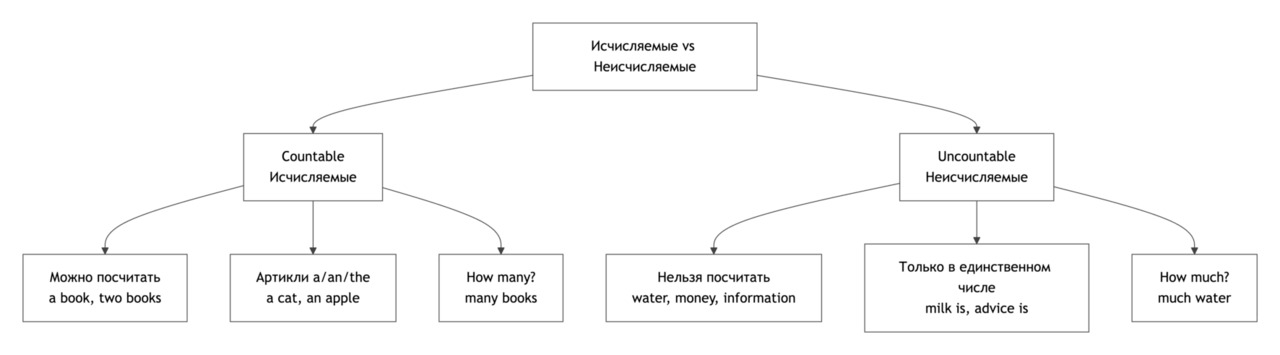
В английском языке существительные делятся на исчисляемые (countable) и неисчисляемые (uncountable).
1. Countable nouns (исчисляемые)
Это предметы, которые можно посчитать.
Есть единственное и множественное число.
Перед существительными можно использовать a / an для единственного числа:
I have a book. — У меня есть книга.
She bought an apple. — Она купила яблоко.
Множественное число образуется обычно добавлением -s / -es:
books, apples, boxes
Можно использовать слова-маркеры: many, a few, several
I have many books. — У меня много книг.
2. Uncountable nouns (неисчисляемые)
Это вещества, материалы, абстрактные понятия, которые нельзя посчитать.
Не имеют множественного числа и не используют a / an.
I drink water every day. — Я пью воду каждый день.
She loves music. — Она любит музыку.
Можно использовать слова-маркеры: much, a little, some
There isn’t much milk left. — Молока осталось немного.
Советы для школьников:
Если можно посчитать предметы — countable.
Если речь о жидкости, пище, материал, абстрактной идее — uncountable.
Используй правильные слова-маркеры, чтобы строить грамматически верные предложения.
Story
A student is preparing breakfast in the kitchen. He takes two eggs from the fridge and puts them in a pan. He also adds some milk to make an omelet. His sister drinks a glass of water and eats two slices of bread. They both love music, so she plays some music while they eat.
Later, the student goes to the shop. He buys a few apples, some cheese, and a bottle of juice. The shop is full of people, but he manages to buy everything he needs. On the way home, he sees his friend and gives him a sandwich and some chocolate.
At home, the student reflects on what he bought and ate. He notices the difference between countable and uncountable nouns. Eggs, apples, and sandwiches are countable because we can count them. Milk, music, cheese, and chocolate are uncountable because we cannot count them. Understanding this difference helps him speak and write more accurately in English.
Useful Words and Expressions
egg — яйцо
a few eggs — несколько яиц
milk — молоко
a glass of water — стакан воды
bread — хлеб
slice of bread — кусок хлеба
music — музыка
a few apples — несколько яблок
cheese — сыр
a bottle of juice — бутылка сока
shop — магазин
bottle — бутылка
sandwich — сэндвич
chocolate — шоколад
eat breakfast — завтракать
prepare breakfast — готовить завтрак
take — взять
put — положить
notice — замечать
countable / uncountable — исчисляемый / неисчисляемый
Exercises
Exercise 1. Fill in the blanks with a few, some, much, or many.
I bought ___ apples at the shop.
There isn’t ___ milk in the fridge.
She ate ___ slices of bread for breakfast.
We have ___ cheese left.
How ___ eggs do you need for the recipe?
Exercise 2. Multiple choice.
Which noun is uncountable?
a) apple
b) bread
c) sandwich
Which noun is countable?
a) water
b) juice
c) egg
Choose the correct sentence:
a) I have a music lesson.
b) I listen to some music every day.
Exercise 3. Answer the questions.
What countable nouns do you eat every day?
What uncountable nouns do you drink or eat every day?
How many apples do you usually buy?
Do you like cheese or chocolate more? Why?
Can you give examples of countable and uncountable nouns at home?
Answer Key
Exercise 1
1 — a few
2 — much
3 — a few
4 — some
5 — many
Exercise 2
1 — b
2 — c
3 — b
Exercise 3 (Sample Answers)
I eat eggs, apples, and sandwiches every day.
I drink milk and water, and I eat cheese and chocolate.
I usually buy three or four apples.
I like chocolate more because it is sweet and tasty.
Countable: books, chairs, pens; Uncountable: water, rice, music.
Mini Tips
Если можно посчитать предмет — countable: используем a / an, many, a few.
Если нельзя посчитать — uncountable: используем some, much, a little.
Для неисчисляемых можно использовать единицы измерения: a glass of, a bottle of, a slice of.
Практикуйся, описывая еду, напитки и предметы вокруг тебя.
Articles: A, An, The and Zero Article
Grammar Focus
В английском языке артикли помогают уточнять существительные. Существуют неопределённые (a, an), определённый (the) и нулевой артикль (zero article).
1. A / An (неопределённые артикли)
Используются с исчисляемыми существительными в единственном числе, когда мы говорим о предмете впервые или не уточняем его.
a перед согласными звуками:
I have a book. — У меня есть книга.
an перед гласными звуками:
She ate an apple. — Она съела яблоко.
2. The (определённый артикль)
Используется, когда мы говорим о конкретном предмете, известном собеседнику.
Также употребляется с уникальными предметами: the sun, the moon.
Примеры:
The book on the table is mine. — Книга на столе моя.
I watched the film you recommended. — Я посмотрел фильм, который ты порекомендовал.
3. Zero Article (нулевой артикль)
Не используется с существительными во множественном числе и неисчисляемыми существительными, когда говорим о них в общем смысле.
Примеры:
Books are useful. — Книги полезны.
Water is necessary for life. — Вода необходима для жизни.
Также нулевой артикль используется с именами городов, стран, материков, языков: London, Russia, English.
Советы для школьников:
A / An — первый раз, любой предмет.
Бесплатный фрагмент закончился.
Купите книгу, чтобы продолжить чтение.